Induction Motor Torque Formula
ω m Speed in rmin. τ ind Induced torque in Nm.

Torque Equation Of Three Phase Induction Motor Electrical4u
The slip is defined as the ratio of difference of synchronous speed and actual rotor speed to the synchronous speed of the machine.
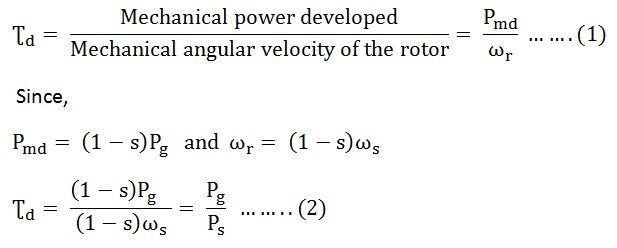
. τ ind 10 hp 746 kWhp 1500 rmin 2 π radr 1 min60 s 4749 Nm. The relative stator to rotor leakage reactance of standard Design B cage induction motors is. τ 3 I 2 2 R 2 s ω s.
E 2 Rotor EMF per phase at a standstill. X 2 Rotor Reactance Per Phase. At synchronous speed s 0 and hence developed torque Ʈd 0.
Nr rated rotational speed revmin rpm In metric units the rated torque can be expressed as. We know that at the start the rotor speed N is zero. T ind 1-sP AG 1-sw sync.
And torque-slip equation 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 3 R S X P V R S X X X X R X X X V sync TH TH TH sync AG ind M M TH TH M M TH Z W I. In imperial units the Full-load Torque can be expressed as. Substitute the values in the above formulas.
K 3 2 Φ n s. Terms used in Motor Torque Equations and formulas. At the start condition the value of s 1.
I L S start 3 V T. T 5252 Php nr 1 where. S b breakdown or pull-out slip.
V supply voltage. Substituting the expression of P 2 in equation 1 we getTorque Where. Ie if you are running y of load then the torque would be T 1732 x V x I x pf x y 2 x pi x N rpm 60 here V rated voltage.
Substituting to write the air gap power in terms of the rotor current the torque can now be written in terms of the rotor current and slip giving the induction motor torque equation. The above-given equation of torque can also be defined in the shape of slip and power air gap losses. The above equation is the torque equation for an induction motor under running condition.
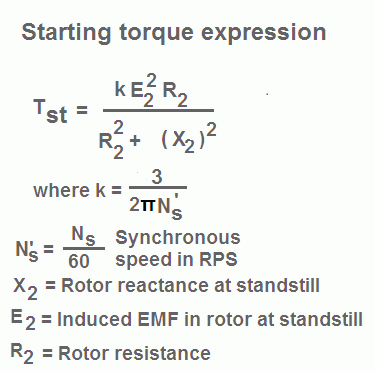
So the equation of starting torque is easily obtained by simply putting the value of s 1 in the equation of torque of the three phase induction motor The starting torque is also known as standstill torque. T 9550 PkW nr 2 where. τ ind P ω m.
T 1732 x V x I x pf 2 x pi x N rpm 60 V Input AC Voltage in volts line to line voltage I Input AC Current in amps. Induction Motor Equations ENGN1931F Spring 2017 4 where τ R R R L R is the rotor time constant. The stator supply voltage.
Also while reducing the motor power the torque will be reduced. Torque Equation at Synchronous Speed. N s Synchronous speed.
There are two equivalent forms of the torque expression here. Torque Power and Speed. K Constant 3602π N s.
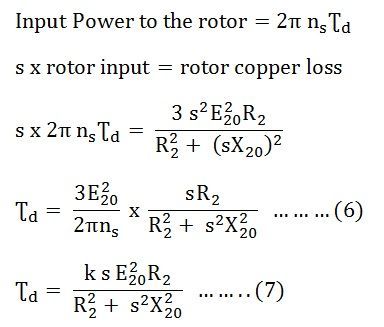
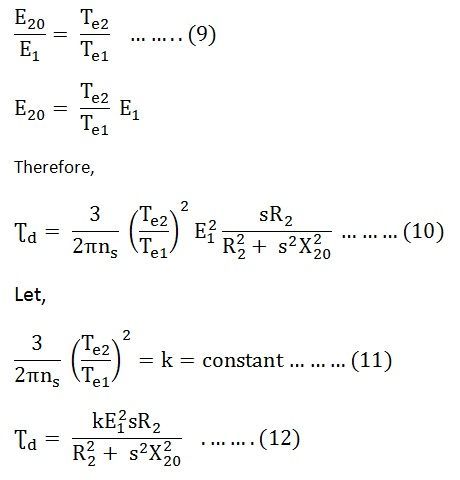
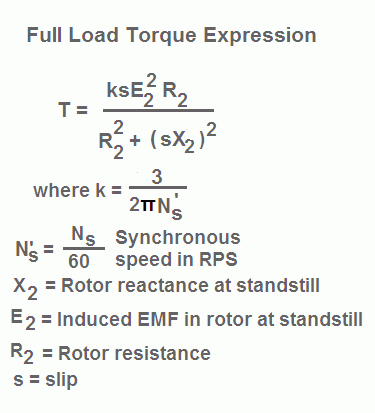
T k s E 22 R 2 R 22 s X 2 2. Formula to find slip n s n x 100n s. T ɸ I 2 cosɸ 2 OR T k ɸ I 2 cosɸ 2.
X s X r 04 06 displaystyle frac X_ text s X_ text rapprox frac 04 06. Thus torque at any speed. E 1 stator voltage or input voltage.
7 where k Constant of proportionality. After putting the slip equation in induced torque equation get the expression of the maximum torque. Therefore the starting is obtained by putting the value of s 1 in the equation 6 we get.
So torque developed at any load condition can be obtained by knowing the slip of the induction motor at that load condition. For many induction motors the average torque drops a bit as it accelerates and then rises to a peak value of torque known as the pull-out or breakdown torque. Neglecting stator resistance an induction motors torque curve reduces to the Kloss equation.
This is a constant torque as shown on the median line in Fig. P power in kW. The normal operating region for the induction motor is the nearly linear portion between rated speed and synchronous speed shown by the heavy line.
This equation is particularly very valuable as It explains the induced torque t ind in form of air-gap power P AG and synchronous speed W sync which does not fluctuate. For three phase AC motor torque formula. T full load torque lb ft Php rated horsepower.
The above equation for torque in terms of rotor current and mechanical slip speed is commonly used. In the full load torque expression expression as written above E2 the rotor induced EMF is proportional E1 ie. S slip of the motor.
Where ɸ flux per stator pole I 2 rotor current at standstill ɸ 2 angle between rotor emf and rotor current k a constant. T 5252 Php nr 1 How do you calculate full load torque of an induction motor. Starting Torque Of Induction Motor.
Torque of a three phase induction motor is proportional to flux per stator pole rotor current and the power factor of the rotor. Developed torque Synchronous speed Rotor speed Power transfer from stator to rotor air gap power Total mechanical power developed by rotor 1 2. Find the shaft torque of the 10 hp induction motor whose rotor speed is 1500 rmin.
6 Using 4 5 6 in equation 1. The constant k is provided to be 32 for three phase induction motor. Starting torque is the torque produced by induction motor when it starts.
T ind 3V TH R 2 s W sync R TH R 2 s 2 X TH X 2 2 This induced torque equation we have determined in the last article which is Derivation of the Induction Motor Induced-Torque Equation you can read it to get this expression. And cos Φ2r R 2 Z 2r R 2 Φ R 22 s X 2 2. The torque slip curve for an induction motor gives us the information about the variation of torque with the slip.
K rotorstator turn ration per Phase. The starting torque is also known as the Standstill Torque. Let us define some parameters to find the torque produce by the induction motor.
R 2 Rotor Resistance Per Phase.

Torque Equation Of Three Phase Induction Motor Electrical4u

Torque Equation Of Three Phase Induction Motor Electrical4u

Gate Ese Three Phase Induction Motor Chapter 3 Offered By Unacademy
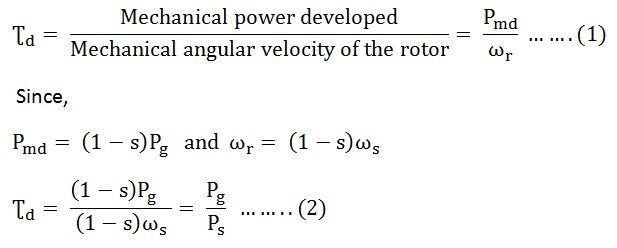
Torque Equation Of An Induction Motor Starting Torque Circuit Globe
Torque Equation Of An Induction Motor Starting Torque Circuit Globe

Induction Motor Starting Torque Equation Come4concepts
Torque Equation Of An Induction Motor Starting Torque Circuit Globe
0 Response to "Induction Motor Torque Formula"
Post a Comment